Right triangles have one right angle. In Euclidean geometry, for right triangles, sum of squares of two shorter sides equals hypotenuse squared {Pythagorean theorem}: c^2 = a^2 + b^2.
proof
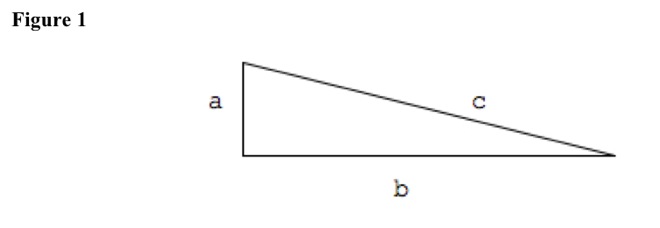
To prove theorem, use geometric construction. Use only straightedge and compass to draw new lines and angles. See Figure 1.
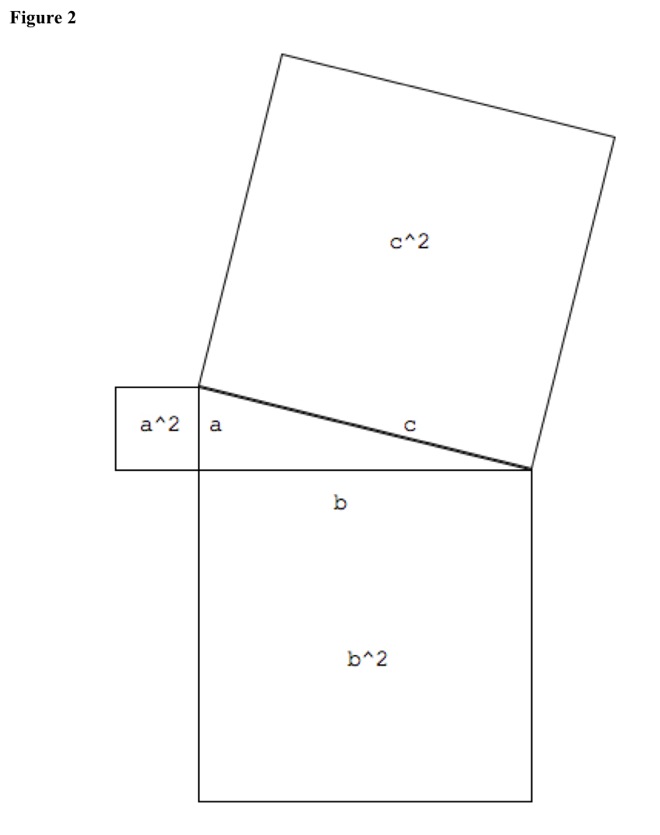
Square sides. See Figure 2.
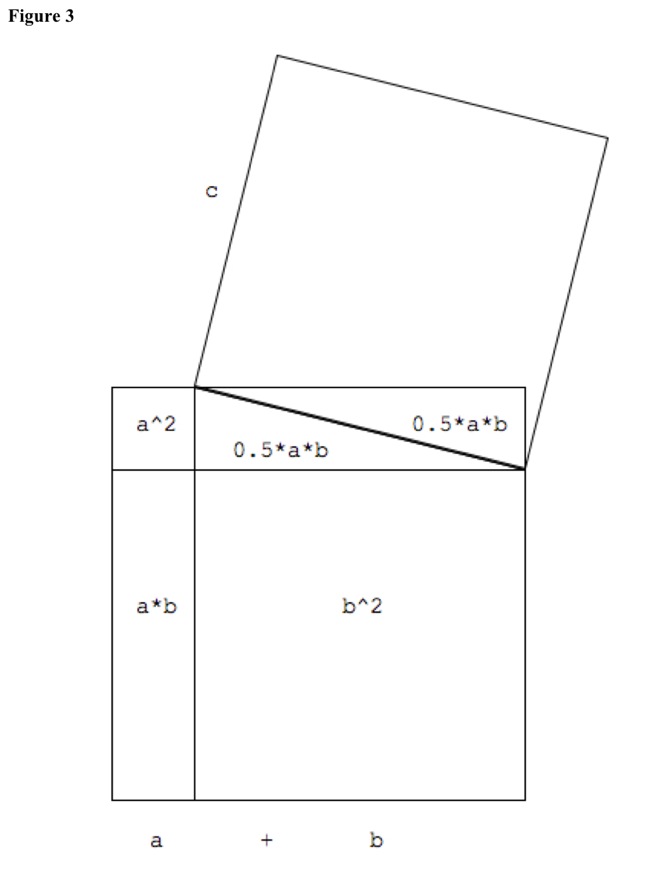
Add original triangle of size 0.5 * a * b, triangle of size 0.5 * a * b beside it, and rectangle of size a*b to squares of sides, to make square of sum of sides and complete the square: (a + b)^2. See Figure 3. (a + b)^2 = a^2 + b^2 + a*b + 0.5 * a * b + 0.5 * a * b = a^2 + b^2 + 2*a*b.
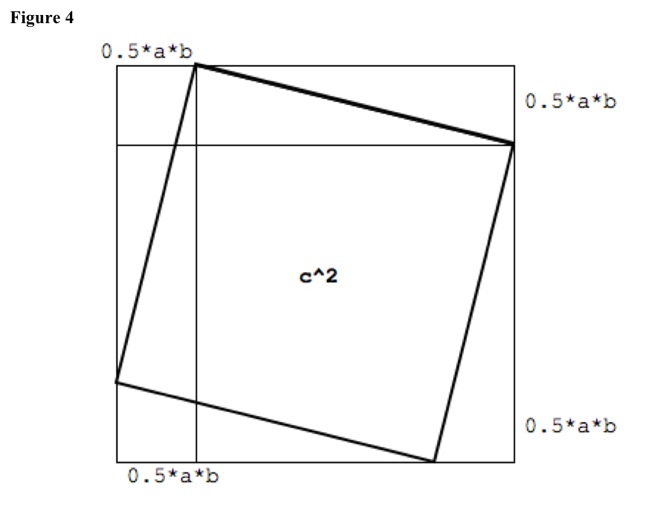
Flip hypotenuse square into square of sum of sides. See Figure 4. c^2 + 4 * (0.5 * a * b) = (a + b)^2. c^2 + 2*a*b = a^ + 2*a*b + b^2. c^2 = a^ + b^2. Hypotenuse squared equals sum of squares of two shorter sides.




Mathematical Sciences>Geometry>Plane>Polygon>Kinds>Triangle
3-Geometry-Plane-Polygon-Kinds-Triangle
Outline of Knowledge Database Home Page
Description of Outline of Knowledge Database
Date Modified: 2022.0224