
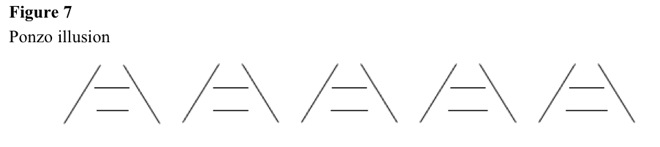
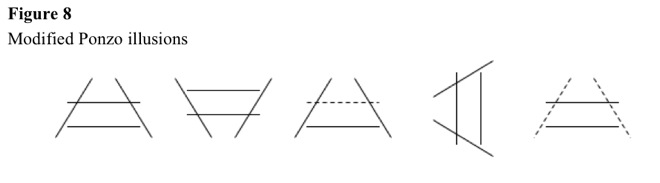
Illusions {illusion} are perceptions that differ from actual metric measurements. Brain uses rules to interpret sense signals, but rules can have contradictions or ambiguities. Vision sees bent lines, shifted lines, different lengths, or different areas, rather than line or area physical properties. Visual illusions are typically depth-perception errors [Frisby, 1979] [Gregory, 1972] [Heydt et al., 1984] [Kanizsa, 1979] [Peterhans and Heydt, 1991].
perception
Illusion, hallucination, and perception sense qualities do not differ. Mind typically does not notice illusions.
neural channels
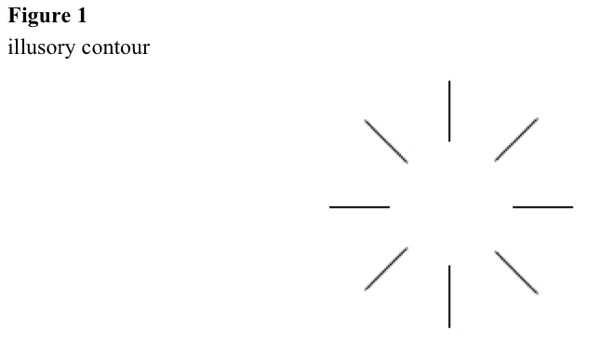
Illusory edges and surfaces appear, because neural channels differ for movement and position. See Figure 1 and Figure 2.
contrast illusions
Contrast can cause illusions. Adelson illusion has grid of lighter and darker squares, making same-gray squares look different. Craik-O'Brien-Cornsweet illusion has lighter rectangle beside darker rectangle, making contrast enhancement at boundary. Mach bands have boundaries with enhanced contrast. Simultaneous brightness contrast illusions have same-gray squares in white or black backgrounds, looking like different grays. White illusion has black vertical bars with same-gray rectangle behind bars and adjacently and translucently in front of bars, looking like different grays.
color illusions
Color can cause color-contrast illusions and color and brightness illusions. Assimilation illusions have background effects that group same color points differently. Fading dot illusion has a green disk with blue dot in center, which fades with continued looking. Munker illusion has blue vertical bars with same-color rectangle behind bars or adjacently and translucently in front of bars, looking like different colors. Neon disk has an asterisk with half-white and half-red bars, which spins. Stroop effect has the word green in red, the word red in green.
geometric illusions
Geometry causes Ebbinghaus illusion, Müller-Lyer illusion, Ponzo illusion, and Zöllner illusion. Café-wall illusion has a vertically irregularly spaced black squares and white squares grid, making horizontal lines appear tilted. Distorted squares illusion has squares in concentric circles, making tilted lines. Ehrenstein illusion has radial lines with circle below center and square above center, making circle and square lines change alignment. Frazier spiral has concentric circles that look like a spiral in a spiraling background. Men with sunglasses illusion (Akiyoshi Kitaoka) has alternating color-square grid with two alternating vertical or horizontal dots at corners, making vertical and horizontal lines tilted. Midorigame or green turtle (Akiyoshi Kitaoka) has a grid with slightly tilted squares in one direction and a center grid with squares slightly tilted in other direction, making vertical and horizontal lines tilted. Poggendorf illusion has two vertical lines with diagonal line that goes behind space between lines, and two vertical lines with diagonal line that goes behind space between lines and dotted line on one side, making behind look not aligned.
size and depth illusions
Size and depth illusions are Ames room (Adelbert Ames), corridor illusion, impossible staircase (Maurits C. Escher), impossible triangle (Maurits C. Escher), impossible waterfall (Maurits C. Escher), Necker cube, size distortion illusion, and trapezoidal window (Adelbert Ames).
figure illusions
Imagined lines can cause illusions. Illusory circle has a small space between horizontal and vertical lines that do not meet, making a small circle. Illusory triangle has solid figures with cutouts that make angles in needed directions, which appear as corners of triangles with complete sides. Illusory square has solid figures with cutouts that make angles in needed directions, which appear as corners of squares with complete sides.
ambiguous figures
Ambiguous figures are eskimo-little girl seen from back, father-son, rabbit-duck, skull-two dancers, young woman and hag, and vase-goblet.
unstable figures
Figures can have features that randomly appear and disappear. Hermann's grid has horizontal and vertical lines with gaps at intersections, where dark disks appear and disappear. Rotating spiral snakes (Akiyoshi Kitaoka) have spirals, which make faint opposite spirals appear to rotate. Thatcher illusion has smile and eye corners up or down (Peter Thompson).
alternating illusions
Illusions with two forms show perceptual dominance or are bistable illusions. Vase-and-face illusion switches between alternatives.
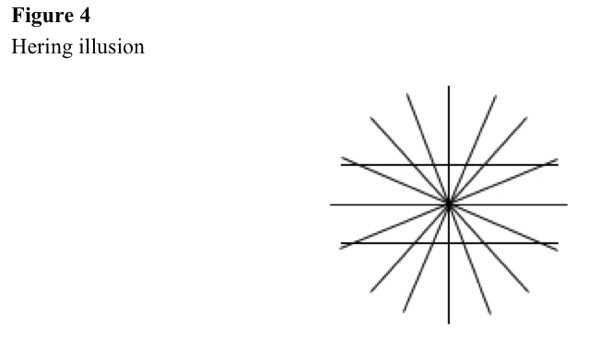
Hering illusion
Radial rays, with two horizontal lines, make illusions. See Figure 4.
music
Music can cause illusions.
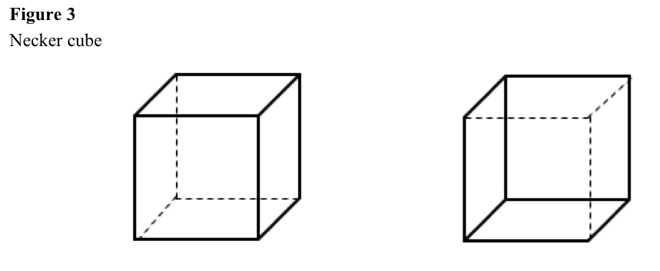
Necker cube
Wire cube at angle makes illusions. See Figure 3.
Ponzo illusion
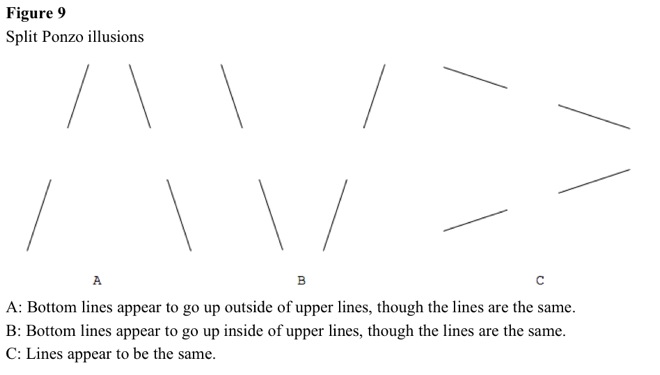
If railroad tracks and ties lead into distance, and two horizontal bars, even with different colors, are at different distances, farther bar appears longer (Mario Ponzo) [1913]. See Figure 7. See Figure 8 for modified Ponzo illusions. See Figure 9 for split Ponzo illusions. Perhaps, line tilt, rather than depth perception, causes Ponzo illusion.
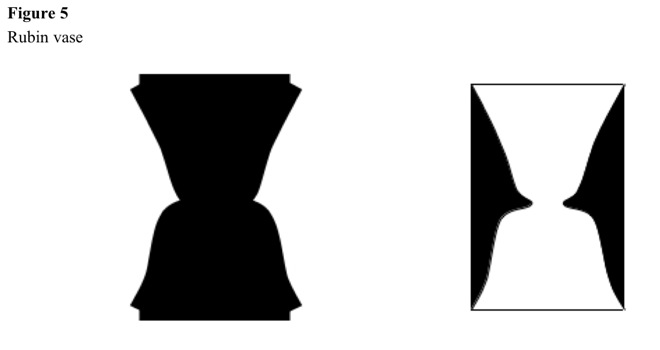
Rubin vase
Central vase has profiles that are symmetrical faces (Edgar Rubin). See Figure 5.
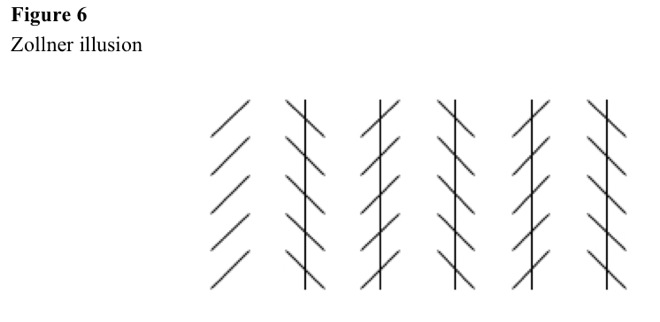
Zollner illusion
Vertical lines have equally spaced parallel line segments at 45-degree angles. See Figure 6.






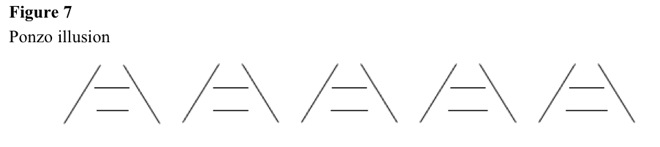
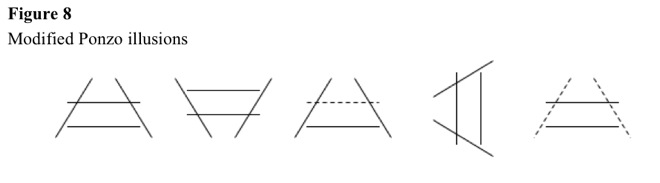

Consciousness>Consciousness>Sense>Vision>Illusions
1-Consciousness-Sense-Vision-Illusions
Outline of Knowledge Database Home Page
Description of Outline of Knowledge Database
Date Modified: 2022.0224